Ransomware is a type of malware that demands some form of payment from the victim in order to recover control of their computer and data. The payment is usually demanded in a virtual currency, such as bitcoin – this means the cybercriminals identity remains anonymous and difficult to trace.
Unlike usual cyber-attacks, the victim is notified that they are under attack and is given instructions on how to recover from the attack via payment. This payment usually comes with a deadline. If not paid in time as requested, the victims files are encrypted.
How its done
There are multiple ways ransomware can access a computer. Infected software apps, infected external storage devices and compromised websites are all ways hackers can encrypt your data for ransom.
One of the most common ways ransomware attacks can be spread is through malicious email attachments. Malicious email attachments will have an attachment disguised as a legitimate file or a URL link. If either the attachment or link is opened the file will begin encrypting files instantly.
Once the victim’s files have been taken over, they are warned of what is happening through a message presented to them. The only way to decrypt their files is if the victim sends a bitcoin payment to the attacker.
Some attackers may claim to be trustworthy sources meaning the victim may be less likely to report to authorities. However, most attackers don’t take this approach and instead ask for money shamelessly.

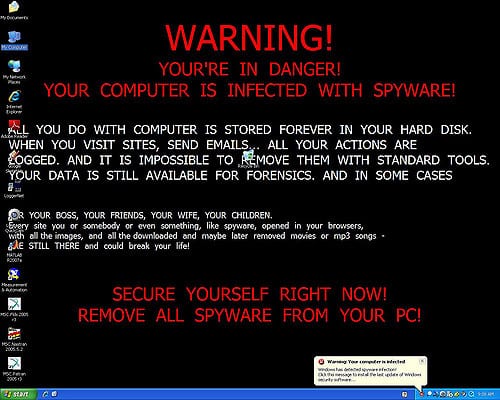
Why you should care
Imagine walking into the office one day to see your computer has been locked with a threatening message on the screen. The message is demanding you make a payment in order to retrieve all your files.
You haven’t completed a back-up recently and could potentially lose critical data to your organisation. Think this won’t happen to you? Think again.
Ransomware attacks are on the rise and every organisation is at risk. Your vulnerability can depend on how attractive your data is to hackers, how you respond, your security and how educated your employees are in identifying breaches.
These types of attacks can lead to severe consequences on your business. Potentially impacting your business’s financial performance, reputation and productivity. Organisations with critical data will remain a prime ransomware target. But whatever your size or industry, it’s important to always be vigilant.
Examples of ransomware:
- WannaCry – This ransomware attack was designed to exploit a vulnerability in Windows. This highlights the issue of how operating on outdated systems could leave you vulnerable to attack. An attack in 2017 affected 230,000 computers globally, hitting a third of hospital trusts in the UK and costing the NHS millions.
- CryptoLocker –Requires cryptocurrency for payment (Bitcoin) and is spread through infected email attachments. Once this is on your computer, it will search for valuable files and hold them to ransom. Cryptolocker is ransomware that was first seen in 2007 and is thought to have affected around 500,000 computers.
- BadRabbit – This attack was deployed back in 2017 using a method called a ‘drive-by’ attack. This involves victims visiting what appears to be a legitimate website but instead the site has been compromised by the cyber criminal. Bad rabbit used a fake request to install Adobe Flash as a malware dropper to spread infection. Victims clicked this without realising it was actually malware in disguise.
- Troldesh – This ransomware attack is spread via spam emails with infected URLS or attachments. Attackers communicate with users directly to demand ransoms. Cyber criminals have even negotiated discounts for victims because they’re able to communicate with each other.
HOW TO PREVENT ATTACKS
REGULAR UPDATES
Keep operating systems patched and up to date to ensure more secure software. Each time you update to the latest security patches, you will maximise ransomware prevention.
Back up your files
Backing up your files is a good way to secure yourself from ransomware. While it won’t stop an attack, it can make the damage caused much less significant as all data can be restored to a previous save point.
Educate your staff
It’s important to educate your staff on the threat landscape. Get them into the habit of being vigilant so they can spot and report any potential breaches before they become a problem.

Technology solutions
Investing in good technology like Cisco Umbrella will help you avoid threats before they even hit your network. It integrates easily with your existing security stack & delivers live threat intelligence about current & emerging threats. With Umbrella, you can stop phishing & malware attacks earlier, identify already infected devices faster & prevent data ex-filtration.
It’s one of the quickest security features you can apply to your network. Because it is delivered from the cloud, there is no hardware to install or software to manually update. So you can protect all of your users in minutes
Try Cisco Umbrella FREE for 14 days & benefit from cutting edge security at the tap of a button.





Recent Comments